.png)
HOCIntelligentTechnologyGroup
Faculty, BIG DATA (information), Large language model(LLM), Generative Pre-trained Transforme model(GPT), Research Lab's "FBLGR Quality" is a leading company,AI Science and Technology Innovation for Global Sustainable Development.
Security,DX, ICT, AI, Agriculture, Medical, Human Resource Development, Future Prediction, SDGs, etc.









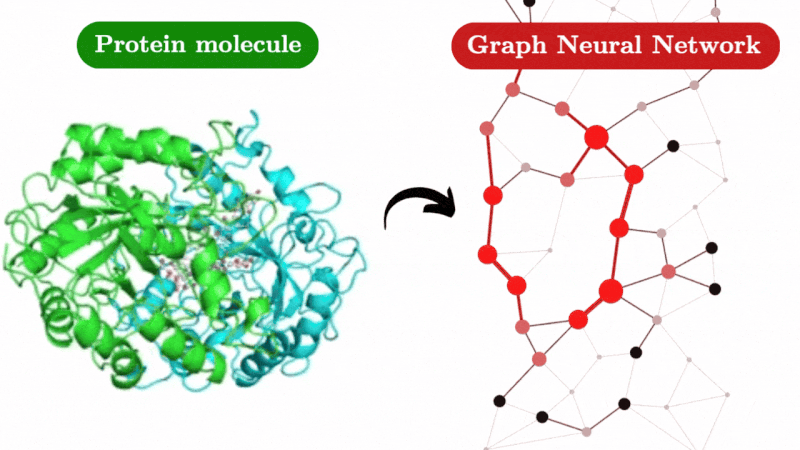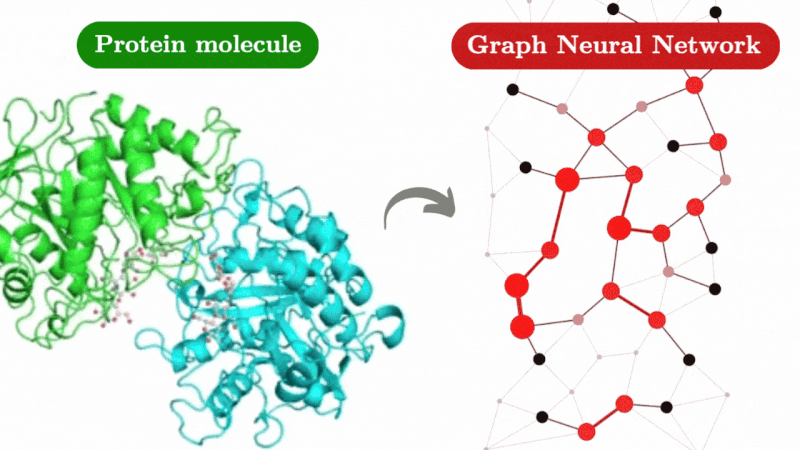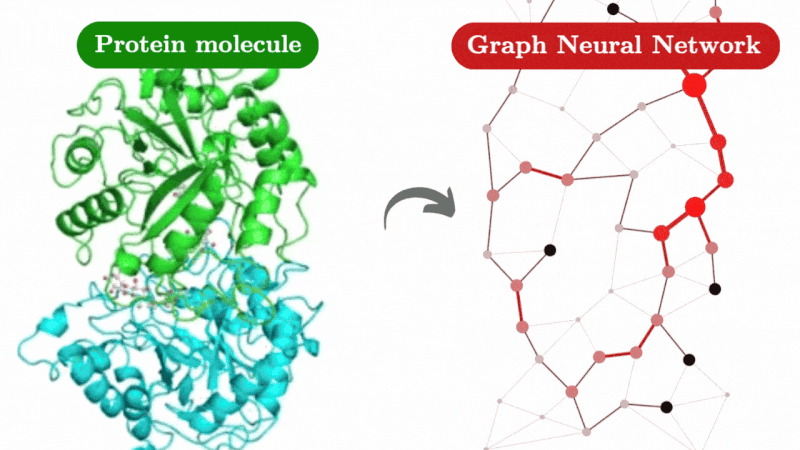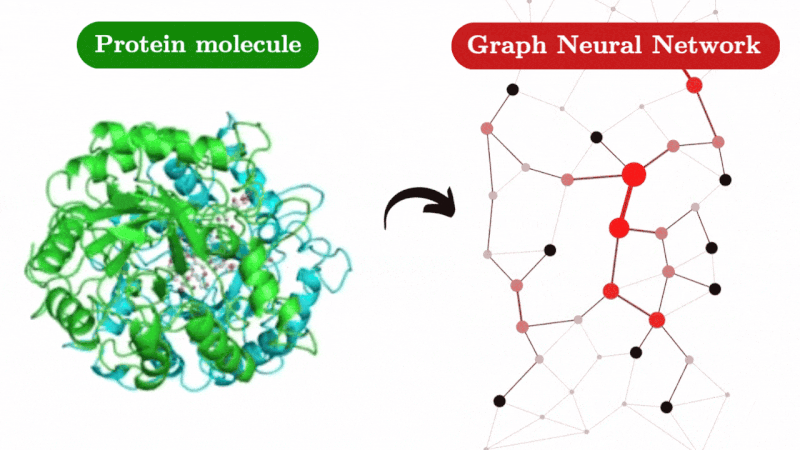
病気の治療プロセス全体をシミュレートするシミュラクリウム「エージェント・ホスピタル」について紹介します。このシミュラクリウムでは、全ての患者、看護師、医師が大規模言語モデル(LLM)によって駆動される自律エージェントです。私たちの中心的な目標は、医師エージェントがシミュラクリウム内で病気の治療方法を学習できるようにすることです。そのために、「MedAgent-Zero」という手法を提案します。このシミュラクリウムは、知識ベースとLLMに基づいて病気の発症や進行をシミュレートできるため、医師エージェントは成功事例や失敗事例から経験を蓄積し続けることができます。シミュレーション実験では、医師エージェントの治療パフォーマンスがさまざまなタスクで一貫して向上することが示されています。さらに興味深いことに、エージェント・ホスピタルで医師エージェントが獲得した知識は、実際の医療ベンチマークにも適用可能であることが確認されました。約一万人の患者を治療した後(実際の医師はこの経験を積むのに2年以上かかることがあります)、進化した医師エージェントは主要な呼吸器疾患をカバーするMedQAデータセットのサブセットで93.06%の最先端の正確度を達成しました。この研究は、医療シナリオにおけるLLM駆動エージェント技術の応用を進展させるための道を開くものです。








Healthcare


AI(人工知能)を活用したヘルスケア領域のフレームワークを構築するためには、いくつかの重要なステップとコンポーネントが必要です。このフレームワークは、データの取得から解析、結果の応用までをカバーする必要があり、医療の質の向上、診断の精度の向上、効率的な患者管理を目指すものです。以下に、その構築プロセスをステップごとに説明します。
ステップ1: 目的と要件の定義
-
目的の明確化: AIを導入する目的(例:疾患の早期発見、治療法のパーソナライズ、患者のアウトカムの改善など)を明確に定義する。
-
要件の特定: プロジェクトに必要なデータの種類、量、質を特定し、必要な技術的リソースや人材、法的規制への対応を理解する。
ステップ2: データの収集と前処理
-
データ収集: 電子健康記録(EHR)、ウェアラブルデバイス、臨床試験などからデータを収集。
-
データクレンジング: 不足データや外れ値の処理、データの正規化や標準化を行う。
-
データ統合: 異なるソースからのデータを統合して、分析のための一貫したフォーマットを確保する。
ステップ3: モデルの開発と検証
-
モデル開発: 機械学習またはディープラーニングモデルを開発し、病状の予測、診断支援、治療効果の予測などに使用。
-
クロスバリデーション: データセットを使用してモデルの有効性を検証し、過学習を避ける。
-
性能評価: 精度、再現率、F1スコアなどの指標を用いてモデルの性能を評価。
ステップ4: 実装と統合
-
システム統合: AIモデルを既存の医療システムと統合し、実際の臨床環境での動作を確認。
-
ユーザートレーニング: 医療従事者がAIシステムを効果的に利用できるようにトレーニングプログラムを提供。
-
監視とメンテナンス: AIシステムのパフォーマンスを継続的に監視し、必要に応じてモデルの再トレーニングやアップデートを行う。
ステップ5: 倫理的および法的考慮事項
-
プライバシー保護: 患者のデータプライバシーを保護するための措置を講じる。
-
倫理的なガイドライン: AIの使用が医療倫理に準拠していることを保証。
-
法的規制の遵守: 医療に関する法律、データ保護法などの関連法規を遵守する。
このフレームワークは、様々なヘルスケアのニーズに対応するための基本的なガイドラインを提供しますが、各プロジェクトの具体的な目的や環境に応じてカスタマイズが必要です。AI技術の急速な進展に伴い、持続的な学習と適応が成功の鍵となります。
4
生成AIでヘルスケア領域フレームワークをpythonで作ってください
ChatGPT
Pythonを使用してAIヘルスケア領域のフレームワークを構築するための基本的なプログラム構造を提供します。このフレームワークは、データの読み込み、前処理、モデルの訓練、評価、予測までのプロセスをカバーします。ここでは、Pythonの機械学習ライブラリであるscikit-learnを使用しますが、より複雑なニューラルネットワークモデルが必要な場合は、TensorFlowやPyTorchの利用を検討することが推奨されます。
ステップ 1: 必要なライブラリのインポート
python
コードをコピーする
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, accuracy_score
ステップ 2: データの読み込みと前処理
python
コードをコピーする
# データの読み込み
data = pd.read_csv('health_data.csv')
# データの前処理
# NaN値の処理
data.fillna(data.mean(), inplace=True)
# フィーチャとターゲットの分離
X = data.drop('target', axis=1)
y = data['target']
# データの標準化
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X)
# データセットの分割
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_scaled, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
ステップ 3: モデルの訓練
python
コードをコピーする
# モデルの訓練
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
ステップ 4: モデルの評価
python
コードをコピーする
# テストデータに対する予測
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# 評価
print("Accuracy:", accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred))
print("Classification Report:\n", classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
ステップ 5: 新しいデータでの予測
python
コードをコピーする
# 新しいデータでの予測
def make_prediction(new_data):
new_data_scaled = scaler.transform(new_data)
prediction = model.predict(new_data_scaled)
return prediction
# 新しいデータの例
new_data = np.array([[5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2]])
print("Prediction:", make_prediction(new_data))
このコードは、ヘルスケアデータセットに基づいてランダムフォレスト分類器を訓練し、評価するための基本的なフレームワークを提供します。実際の用途に合わせて、データセットの特性や必要な処理、使用するモデルの種類などをカスタマイズする必要があります。また、モデルの性能向上や過学習の防止のために、ハイパーパラメータのチューニングやクロスバリデーションなどの高度な技術を適用することが考えられます。
生成AIでヘルスケア領域ヘルスケア食品の品質評価システムフレームワークを作ってください
ChatGPT
ヘルスケア食品の品質評価システムをAIを用いて構築する場合、データ駆動型のアプローチを採用し、品質関連の指標を自動的に分析・評価することが可能です。このシステムは、食品の安全性、栄養成分、消費者の健康に与える影響など、複数の側面から品質を評価します。以下は、Pythonを使用してヘルスケア食品の品質評価システムの基本フレームワークを構築するためのステップです。
ステップ 1: 必要なライブラリのインポート
python
コードをコピーする
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.svm import SVC # サポートベクターマシンを使用
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
ステップ 2: データの読み込みと前処理
python
コードをコピーする
# データの読み込み
data = pd.read_csv('health_food_data.csv')
# 不要な列の削除
data.drop(['unnecessary_column'], axis=1, inplace=True)
# データの前処理
data.fillna(data.mean(), inplace=True) # 欠損値の処理
# フィーチャとターゲットの分離
X = data.drop('quality_label', axis=1) # 品質ラベルを除外
y = data['quality_label'] # 品質ラベル
# データの標準化
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_scaled = scaler.fit_transform(X)
# データセットの分割
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_scaled, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
ステップ 3: モデルの訓練と評価
python
コードをコピーする
# モデルの訓練
model = SVC(kernel='linear') # 線形カーネルを使用
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# モデルの評価
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
print("Classification Report:\n", classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
print("Confusion Matrix:\n", confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred))
# Confusion Matrixの可視化
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 7))
sns.heatmap(confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred), annot=True, fmt='g')
plt.xlabel('Predicted')
plt.ylabel('Truth')
plt.show()
ステップ 4: モデルの適用と新しいデータの予測
python
コードをコピーする
# 新しいデータでの予測関数
def predict_quality(new_data):
new_data_scaled = scaler.transform([new_data]) # 新しいデータの標準化
prediction = model.predict(new_data_scaled) # 品質の予測
return prediction
# 予測例
new_sample = [5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2] # 新しいサンプルデータ
predicted_quality = predict_quality(new_sample)
print("Predicted Quality Label:", predicted_quality)
このフレームワークはヘルスケア食品の品質評価の基本的なモデルを提供し、データの前処理、モデルの訓練、評価、新しいデータの予測に関連するコードを含んでいます。このシステムを実際のビジネスや研究で使用する前に、特定の要件や目標に合わせてカスタマイズし、追加の検証や改善を行う必要があります。
4
生成AIでHealth領域ヘルスケア食品の品質評価フレームワークを作ってください
ChatGPT
ヘルスケア食品の品質評価のためのAIフレームワークを構築するプロセスは、データの収集からモデルの適用まで複数のステップを含みます。このフレームワークは、食品の安全性、栄養成分、及び消費者の健康に与える影響を評価するためのものです。ここでは、それぞれのステップを具体的に説明し、必要な技術要素を組み込んでいきます。
ステップ1: 目的と要件の特定
-
目的の明確化: ヘルスケア食品のどの品質属性(栄養価、保存料の使用、有害物質の非存在など)をAIを使って評価するのかを定義する。
-
データ要件の特定: 品質評価に必要なデータタイプ(化学分析データ、消費者フィードバック、製品の成分表など)を特定し、データ収集の方法を決定する。
ステップ2: データ収集と前処理
-
データ収集: 関連するデータソースからデータを収集。例えば、製品の成分データ、生産プロセスの詳細、消費者レビューなど。
-
データクレンジング: 不完全データや外れ値の除去、必要に応じてデータの補完。
-
特徴量エンジニアリング: 栄養成分の比率、保存料の種類や量、自然成分の割合など、品質評価に必要な特徴量を生成。
ステップ3: 分析モデルの構築
-
モデル選択: 分類問題(良/不良)、回帰問題(品質スコア予測)など、目的に応じたモデルを選択。機械学習モデル(ランダムフォレスト、サポートベクターマシン)やディープラーニングモデル(CNN、RNN)を検討。
-
モデル訓練と検証: トレーニングデータを使用してモデルを訓練し、検証データでモデルの性能を評価。
ステップ4: システムの実装と統合
-
APIの開発: 訓練されたモデルをAPIとして実装し、実際の製品テストシステムやウェブアプリケーションと統合。
-
ユーザーインターフェースの開発: 技術者や品質管理担当者が簡単に使用できるユーザーフレンドリーなインターフェースを開発。
ステップ5: 監視と最適化
-
パフォーマンス監視: システムを定期的に監視し、予測精度の低下やデータ入力の問題がないかを確認。
-
フィードバックループの設計: ユーザーや消費者からのフィードバックを収集し、モデルの継続的な改善に活用。
ツールとテクノロジー
-
プログラミング言語: Python、R
-
データ処理ライブラリ: Pandas, NumPy
-
機械学習フレームワーク: scikit-learn, TensorFlow, PyTorch
-
データベース: SQL, NoSQLデータベース
-
ウェブ開発フレームワーク: Flask, Django(API用)
このフレームワークを通じて、ヘルスケア食品の品質評価を科学的かつ体系的に行うことが可能になり、製品の安全性と消費者の信頼を向上させることができます

Agent Hospital
An Agent-Based Simulation Approach to Model Hospital Logistics
Healthcare

AI医者(デジタル医者)を構築するためには、以下の要素を含むシステムを作成する必要があります。
-
ユーザーインターフェース: 症状を入力し、AIの診断結果やアドバイスを受け取るためのインターフェース。
-
症状チェック機能: ユーザーが入力した症状に基づいて診断を行う機能。
-
リアルタイムチャット: ユーザーとAI医者の間でリアルタイムでやり取りできる機能。
-
データベース: 患者の症状や診断結果を保存するためのデータベース。
-
セキュリティ: ユーザーデータの保護とプライバシーの確保。
以下に、これらの要素を組み合わせた基本的なAI医者システムのサンプルコードを示します。このサンプルでは、Flaskを使用してWebアプリケーションを構築し、OpenAIのGPTモデルを利用してAI医者の機能を実装しています。
必要なライブラリのインストール
bash
コードをコピーする
pip install Flask Flask-SocketIO openai Flask-SQLAlchemy
Flaskアプリケーションのコード
app.py
python
コードをコピーする
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, redirect, url_for, session, jsonify
from flask_socketio import SocketIO, emit
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
import openai
from datetime import datetime
app = Flask(__name__)
app.secret_key = 'supersecretkey'
socketio = SocketIO(app)
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'sqlite:///site.db'
db = SQLAlchemy(app)
# OpenAI APIキー設定
openai.api_key = 'your_openai_api_key'
# データベースモデル
class PatientData(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
user_id = db.Column(db.String(150), nullable=False)
date = db.Column(db.String(100), nullable=False)
symptoms = db.Column(db.String(200), nullable=False)
diagnosis = db.Column(db.String(200), nullable=False)
class User(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
username = db.Column(db.String(150), unique=True, nullable=False)
password = db.Column(db.String(150), nullable=False)
# ルートとビュー
@app.route('/')
def home():
return render_template('index.html')
@app.route('/register', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def register():
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.form['username']
password = request.form['password']
user = User(username=username, password=password)
db.session.add(user)
db.session.commit()
return redirect(url_for('login'))
return render_template('register.html')
@app.route('/login', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def login():
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.form['username']
password = request.form['password']
user = User.query.filter_by(username=username, password=password).first()
if user:
session['username'] = username
return redirect(url_for('dashboard'))
return render_template('login.html')
@app.route('/logout')
def logout():
session.pop('username', None)
return redirect(url_for('home'))
@app.route('/dashboard')
def dashboard():
if 'username' in session:
return render_template('dashboard.html', username=session['username'])
return redirect(url_for('login'))
@app.route('/add_symptoms', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def add_symptoms():
if 'username' not in session:
return redirect(url_for('login'))
if request.method == 'POST':
user_id = session['username']
date = datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
symptoms = request.form['symptoms']
# 症状を診断
result = openai.Completion.create(
engine="text-davinci-003",
prompt=f"Patient: {symptoms}\nDoctor:",
max_tokens=150
)
diagnosis = result.choices[0].text.strip()
new_data = PatientData(user_id=user_id, date=date, symptoms=symptoms, diagnosis=diagnosis)
db.session.add(new_data)
db.session.commit()
return render_template('result.html', diagnosis=diagnosis)
return render_template('add_symptoms.html')
@app.route('/history')
def history():
if 'username' not in session:
return redirect(url_for('login'))
user_id = session['username']
data = PatientData.query.filter_by(user_id=user_id).all()
return render_template('history.html', data=data)
@app.route('/chat')
def chat():
if 'username' in session:
return render_template('chat.html', username=session['username'])
return redirect(url_for('login'))
@socketio.on('send_message')
def handle_message(data):
user_message = data['message']
response = openai.Completion.create(
engine="text-davinci-003",
prompt=f"Patient: {user_message}\nDoctor:",
max_tokens=150
)
doctor_message = response.choices[0].text.strip()
emit('receive_message', {'message': doctor_message}, broadcast=True)
if __name__ == '__main__':
db.create_all()
socketio.run(app, debug=True)
テンプレートファイル
-
templates/index.html
html
コードをコピーする
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>AI Doctor</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to AI Doctor</h1>
<a href="/register">Register</a> | <a href="/login">Login</a>
</body>
</html>
-
templates/register.html
html
コードをコピーする
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Register</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Register</h1>
<form action="/register" method="post">
Username: <input type="text" name="username"><br>
Password: <input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Register">
</form>
</body>
</html>
-
templates/login.html
html
コードをコピーする
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Login</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Login</h1>
<form action="/login" method="post">
Username: <input type="text" name="username"><br>
Password: <input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Login">
</form>
</body>
</html>
-
templates/dashboard.html
html
コードをコピーする
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Dashboard</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome, {{ username }}</h1>
<a href="/add_symptoms">Add Symptoms</a> | <a href="/history">View History</a> | <a href="/chat">Chat with AI Doctor</a> | <a href="/logout">Logout</a>
</body>
</html>
-
templates/add_symptoms.html
html
コードをコピーする
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Add Symptoms</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Add Symptoms</h1>
<form action="/add_symptoms" method="post">
Symptoms: <input type="text" name="symptoms"><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
-
templates/result.html
html
コードをコピーする
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Diagnosis Result</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Diagnosis Result</h1>
<p>Diagnosis: {{ diagnosis }}</p>
<a href="/dashboard">Back to Dashboard</a>
</body>
</html>
-
templates/history.html
html
コードをコピーする
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>History</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>History</h1>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>Date</th>
<th>Symptoms</th>
<th>Diagnosis</th>
</tr>
{% for record in data %}
<tr>
<td>{{ record.date }}</td>
<td>{{ record.symptoms }}</td>
<td>{{ record.diagnosis }}</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</table>
<a href="/dashboard">Back to Dashboard</a>
</body>
</html>
-
templates/chat.html
html
コードをコピーする
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Medical Chat</title>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js"></
ちらがデジタル医者システムの構造図です。各コンポーネントとデータの流れが視覚化されています。
システムの主なコンポーネントは以下の通りです:
-
ユーザーインターフェース: Webおよびモバイルインターフェースで、ユーザーが症状を入力したり、AI医者とチャットしたりすることができます。
-
Webサーバー: Flaskアプリケーションサーバーがユーザーからのリクエストを処理し、インタラクションを管理します。
-
AIモデル: OpenAI GPTモデルを使用して症状の診断とチャットの応答を行い、BERTモデルで症状を分析します。
-
データベース: SQLAlchemyデータベースがユーザーデータ、症状、診断履歴を保存します。
-
リアルタイムチャット: WebSocket(Flask-SocketIO)を使用してリアルタイムチャット通信を実現します。
-
セキュリティ: HTTPSで通信を暗号化し、ユーザーログインとセッション管理のための認証機構を提供します。
-
外部API: 外部の健康データベースやAPIと統合して、診断の精度を向上させます。
-
デプロイメント: AWSやHerokuなどのクラウドサービスにホスティングします。
この図は、各コンポーネントがどのように相互作用するかを示しており、データの流れが矢印で示されています。











デジタル医者やデジタル大学教授のシステムに音声機能を追加するためには、以下の要素が必要です。
-
音声入力: ユーザーが音声で質問や症状を入力できるようにする。
-
音声出力: AIがテキストの回答を音声で返答する。
PythonのFlaskを使用したシステムに音声入力と音声出力を追加するためには、ブラウザのWeb Speech APIを利用して音声入力を取得し、PythonのgTTS(Google Text-to-Speech)ライブラリを利用して音声出力を生成します。
必要なライブラリのインストール
bash
コードをコピーする
pip install Flask Flask-SocketIO openai Flask-SQLAlchemy gTTS
シンプルなAI医者システムに音声機能を追加
app.py
python
コードをコピーする
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, redirect, url_for, session, jsonify, send_file
from flask_socketio import SocketIO, emit
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
import openai
from datetime import datetime
from gtts import gTTS
import os
app = Flask(__name__)
app.secret_key = 'supersecretkey'
socketio = SocketIO(app)
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'sqlite:///site.db'
db = SQLAlchemy(app)
# OpenAI APIキー設定
openai.api_key = 'your_openai_api_key'
# データベースモデル
class PatientData(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
user_id = db.Column(db.String(150), nullable=False)
date = db.Column(db.String(100), nullable=False)
symptoms = db.Column(db.String(200), nullable=False)
diagnosis = db.Column(db.String(200), nullable=False)
class User(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
username = db.Column(db.String(150), unique=True, nullable=False)
password = db.Column(db.String(150), nullable=False)
# ルートとビュー
@app.route('/')
def home():
return render_template('index.html')
@app.route('/register', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def register():
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.form['username']
password = request.form['password']
user = User(username=username, password=password)
db.session.add(user)
db.session.commit()
return redirect(url_for('login'))
return render_template('register.html')
@app.route('/login', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def login():
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.form['username']
password = request.form['password']
user = User.query.filter_by(username=username, password=password).first()
if user:
session['username'] = username
return redirect(url_for('dashboard'))
return render_template('login.html')
@app.route('/logout')
def logout():
session.pop('username', None)
return redirect(url_for('home'))
@app.route('/dashboard')
def dashboard():
if 'username' in session:
return render_template('dashboard.html', username=session['username'])
return redirect(url_for('login'))
@app.route('/add_symptoms', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def add_symptoms():
if 'username' not in session:
return redirect(url_for('login'))
if request.method == 'POST':
user_id = session['username']
date = datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
symptoms = request.form['symptoms']
# 症状を診断
result = openai.Completion.create(
engine="text-davinci-003",
prompt=f"Patient: {symptoms}\nDoctor:",
max_tokens=150
)
diagnosis = result.choices[0].text.strip()
new_data = PatientData(user_id=user_id, date=date, symptoms=symptoms, diagnosis=diagnosis)
db.session.add(new_data)
db.session.commit()
return render_template('result.html', diagnosis=diagnosis)
return render_template('add_symptoms.html')
@app.route('/history')
def history():
if 'username' not in session:
return redirect(url_for('login'))
user_id = session['username']
data = PatientData.query.filter_by(user_id=user_id).all()
return render_template('history.html', data=data)
@app.route('/chat')
def chat():
if 'username' in session:
return render_template('chat.html', username=session['username'])
return redirect(url_for('login'))
@socketio.on('send_message')
def handle_message(data):
user_message = data['message']
response = openai.Completion.create(
engine="text-davinci-003",
prompt=f"Patient: {user_message}\nDoctor:",
max_tokens=150
)
doctor_message = response.choices[0].text.strip()
# 音声出力生成
tts = gTTS(doctor_message, lang='en')
audio_file = f"static/audio/response_{datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d%H%M%S')}.mp3"
tts.save(audio_file)
emit('receive_message', {'message': doctor_message, 'audio': audio_file}, broadcast=True)
if __name__ == '__main__':
db.create_all()
socketio.run(app, debug=True)
テンプレートファイルの追加
-
templates/chat.html
html
コードをコピーする
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Medical Chat</title>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/socket.io/4.0.1/socket.io.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var socket = io();
$('#chat-form').on('submit', function(e){
e.preventDefault();
var userMessage = $('#message-input').val();
$('#messages').append('<div><strong>You:</strong> ' + userMessage + '</div>');
$('#message-input').val('');
socket.emit('send_message', { message: userMessage });
});
socket.on('receive_message', function(data){
$('#messages').append('<div><strong>Doctor:</strong> ' + data.message + '</div>');
var audio = new Audio(data.audio);
audio.play();
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Medical Chat</h1>
<div id="chat-box">
<div id="messages"></div>
</div>
<form id="chat-form">
<input type="text" id="message-input" name="message" placeholder="Enter your message" required>
<button type="submit">Send</button>
</form>
</body>
</html>
このコードは、ユーザーがリアルタイムでAI医者とチャットし、音声で応答を受け取る機能を提供します。音声入力はブラウザのWeb Speech APIを利用して実装できますが、この例では音声出力のみを扱っています。音声入力の実装については以下のようなJavaScriptを利用します。
音声入力の追加(JavaScript)
-
templates/chat.htmlのスクリプト部分に追加
html
コードをコピーする
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
var socket = io();
var recognition = new (window.SpeechRecognition || window.webkitSpeechRecognition)();
recognition.lang = 'en-US';
recognition.interimResults = false;
$('#start-record-btn').on('click', function(){
recognition.start();
});
recognition.onresult = function(event){
var userMessage = event.results[0][0].transcript;
$('#messages').append('<div><strong>You:</strong> ' + userMessage + '</div>');
socket.emit('send_message', { message: userMessage });
};
$('#chat-form').on('submit', function(e){
e.preventDefault();
var userMessage = $('#message-input').val();
$('#messages').append('<div><strong>You:</strong> ' + userMessage + '</div>');
$('#message-input').val('');
socket.emit('send_message', { message: userMessage });
});
socket.on('receive_message', function(data){
$('#messages').append('<div><strong>Doctor:</strong> ' + data.message + '</div>');
var audio = new Audio(data.audio);
audio.play();
});
});
</script>
-
templates/chat.htmlのフォーム部分に追加
html
コードをコピーする
<button type="button" id="start-record-btn">Start Recording</button>
このようにして、ユーザーはボタンをクリックして音声入力を開始し、音声で質問を入力することができます。AI医者はテキストと音声で応答します。
フォームの終わり







連絡先
Abstract:
Agent.Hospital is an open agent-based (software) framework for distributed application in the healthcare domain. Previous appropriation of the Agent.Hospital development is application and examination of agent technology in realistic business scenarios and the identification of further research needs.